FAIL / Epic Fail - Images (1,561 results)
Bathroom with an unblockable window to the kitchen


FAIL / Epic Fail
This hurts my eyes


FAIL / Epic Fail
Why?


FAIL / Epic Fail
Green recycling logo = non-recyclable


FAIL / Epic Fail
High-end coffee pot with too short of a spout
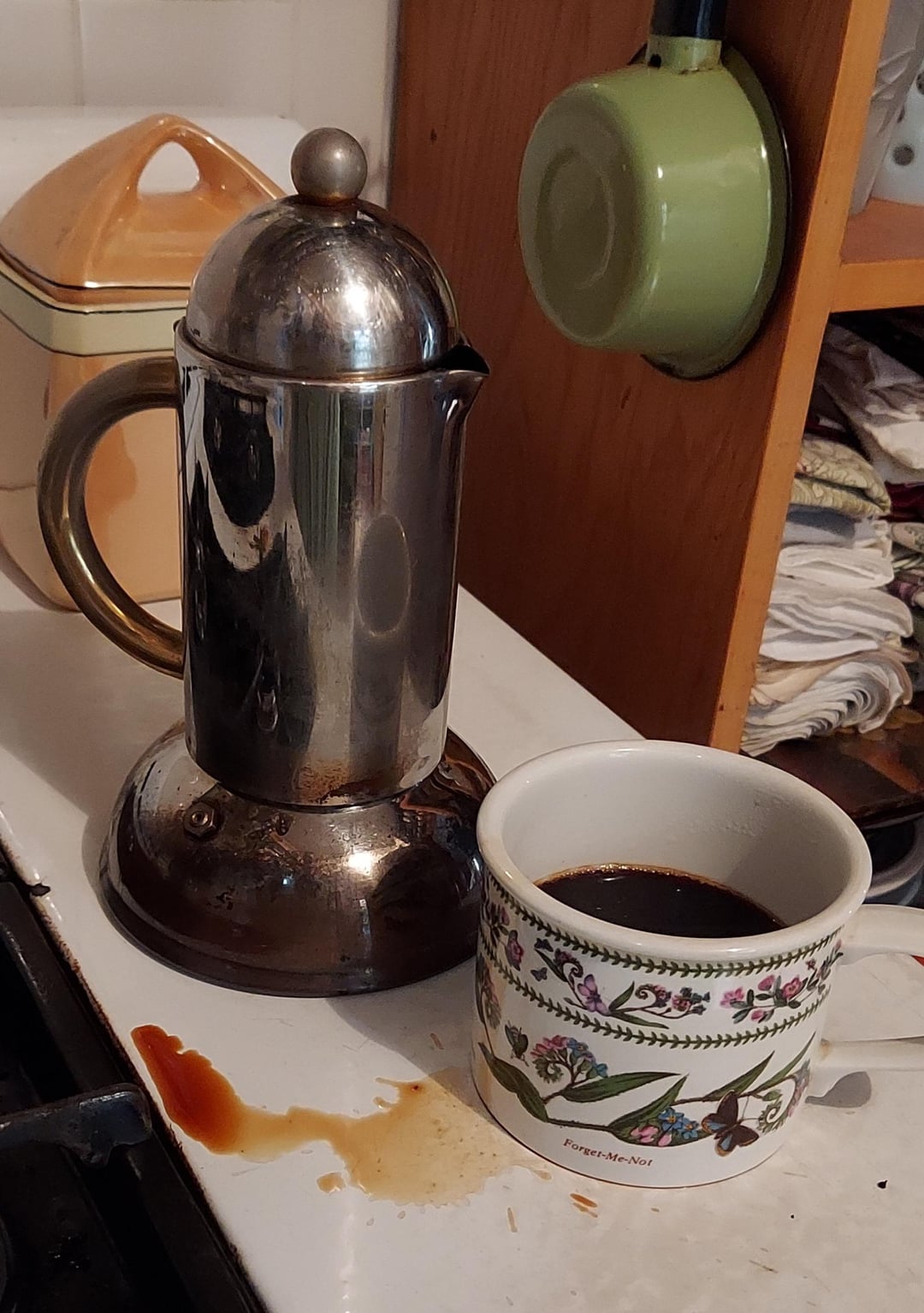


FAIL / Epic Fail
The maze with no solution


FAIL / Epic Fail
In the un


FAIL / Epic Fail
Wedge yourself in the dirtiest corner to wash your hands
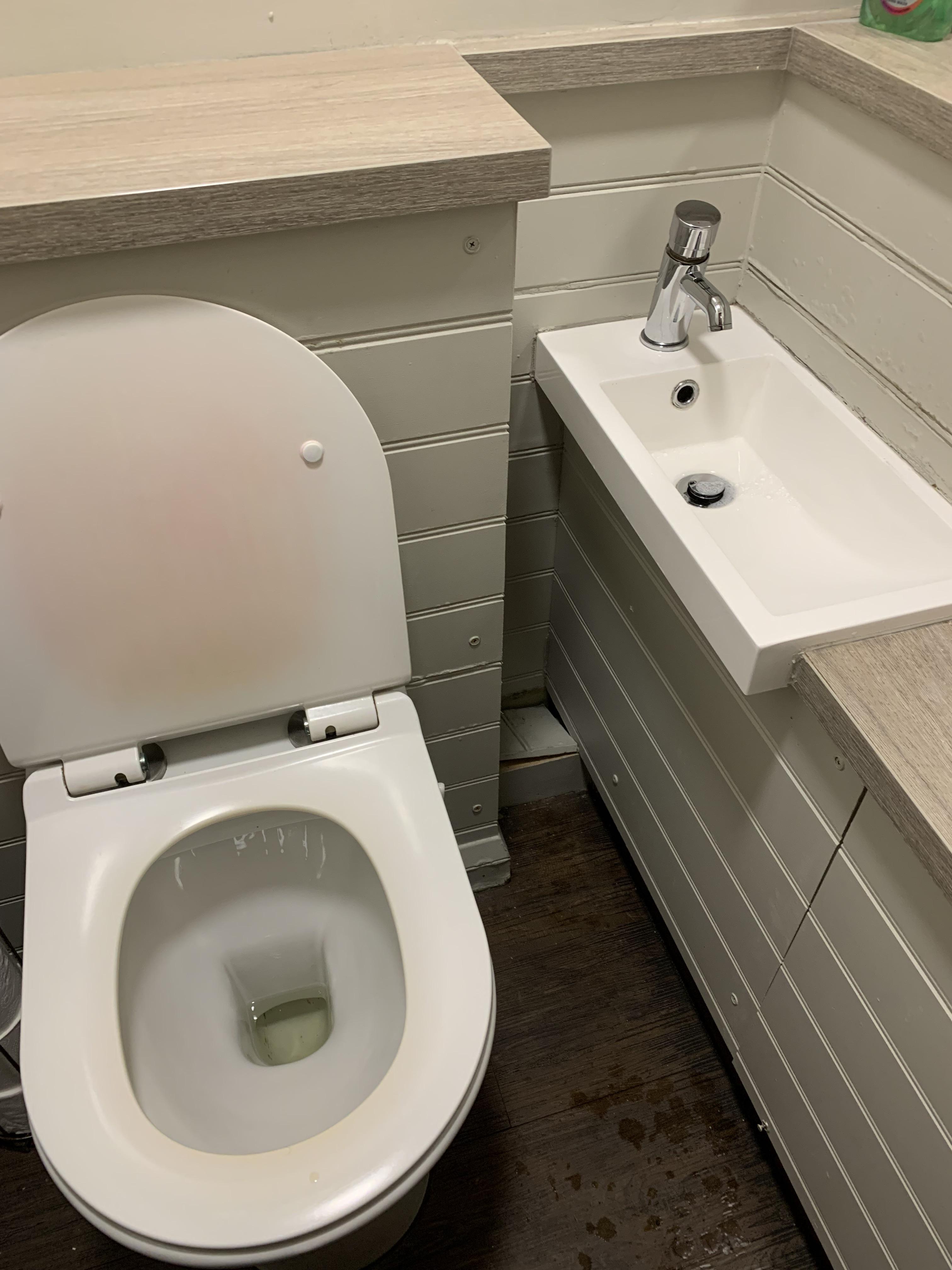


FAIL / Epic Fail
Another handicap ramp blocked by a pole
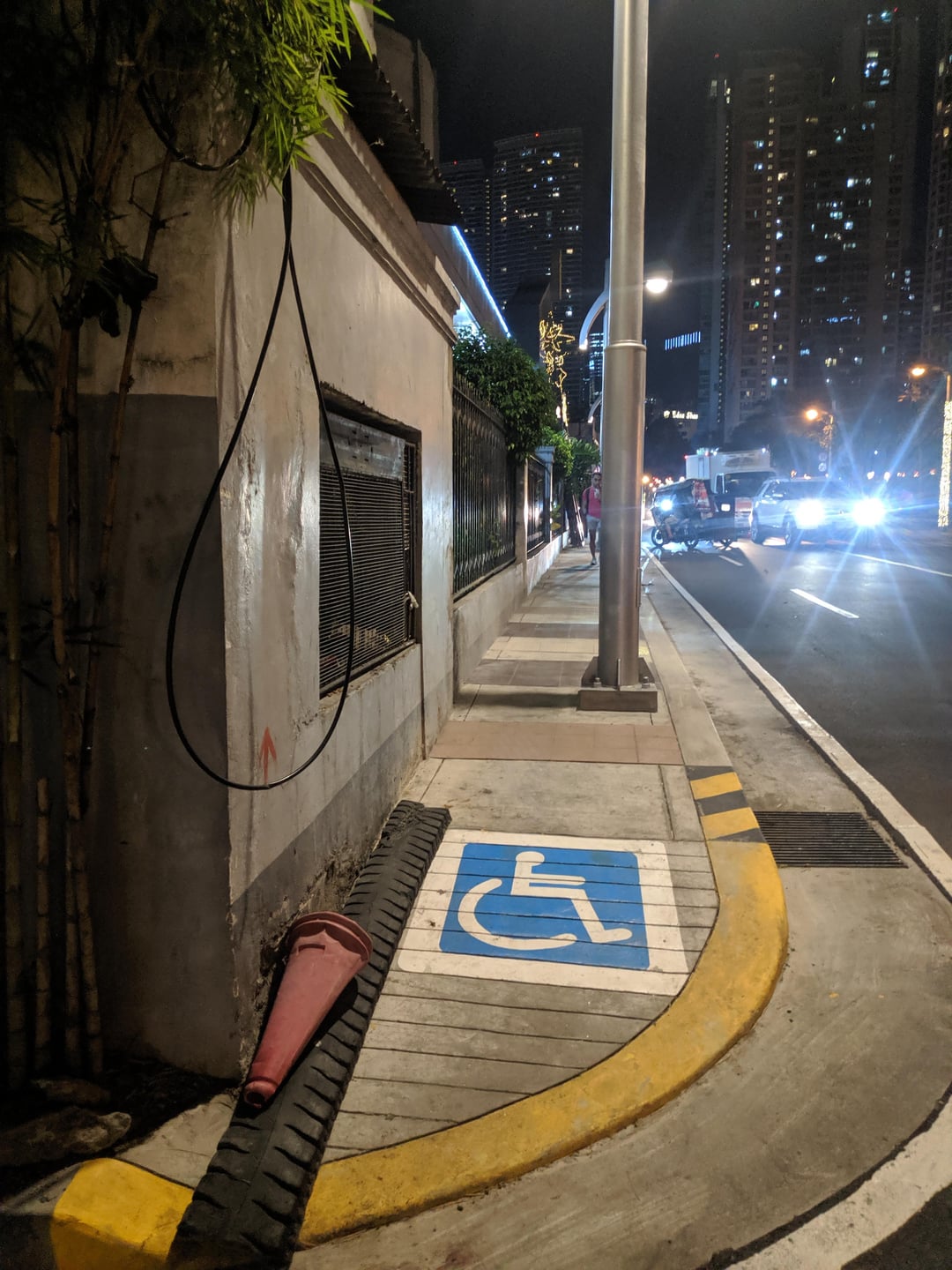


FAIL / Epic Fail
A true best seller


FAIL / Epic Fail
Oops.
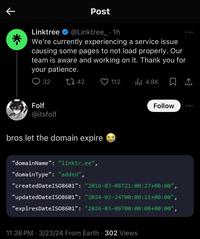

FAIL / Epic Fail
Subtle ways to spot AI might have written the introduction 😀
![ELSEVIER Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Surfaces and Interfaces journal homepage: www.sciencedirect.com/journal/surfaces-and-interfaces The three-dimensional porous mesh structure of Cu-based metal-organic-framework - aramid cellulose separator enhances the electrochemical performance of lithium metal anode batteries Manshu Zhang, 1, Liming Wu, Tao Yang, Bing Zhu, Yangai Liu"." "Beijing Key Laboratory of Materials Utilization of Nonmetallic Minerals and Solid Wastes, National Laboratory of Mineral Materials, School of Materials Science and Technology, China University of Geosciences, Beijing 100083, China b College of Materials & Environmental Engineering, Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou 310036, China SURFACES INTERFACES ARTICLE INFO Keywords: Lithium metal battery Lithium dendrites CUMOF-ANFS separator ABSTRACT Lithium metal, due to its advantages of high theoretical capacity, low density and low electrochemical reaction potential, is used as a negative electrode material for batteries and brings great potential for the next generation of energy storage systems. However, the production of lithium metal dendrites makes the battery life low and poor safety, so lithium dendrites have been the biggest problem of lithium metal batteries. This study shows that the larger specific surface area and more pore structure of Cu-based metal-organic-framework - aramid cellulose (CUMOF-ANFS) composite separator can help to inhibit the formation of lithium dendrites. After 110 cycles at 1 mA/cm², the discharge capacity retention rate of the Li-Cu battery using the CuMOF-ANFS separator is about 96 %. Li-Li batteries can continue to maintain low hysteresis for 2000 h at the same current density. The results show that CUMOF-ANFS composite membrane can inhibit the generation of lithium dendrites and improve the cycle stability and cycle life of the battery. The three-dimensional (3D) porous mesh structure of CuMOF-ANFS separator provides a new perspective for the practical application of lithium metal battery. 1. Introduction Certainly, here is a possible introduction for your topic:Lithium- metal batteries are promising candidates for high-energy-density rechargeable batteries due to their low electrode potentials and high theoretical capacities [1,2]. However, during the cycle, dendrites forming on the lithium metal anode can cause a short circuit, which can affect the safety and life of the battery [3-9]. Therefore, researchers are indeed focusing on various aspects such as negative electrode structure [10], electrolyte additives [11,12], SEI film construction [13,14], and collector modification [15] to inhibit the formation of lithium dendrites. However, using a separator with high mechanical strength and chemical stability is another promising approach to prevent dendrites from infiltrating the cathode. By incorporating a separator with high me- chanical strength, it can act as a physical barrier to impede the growth of dendrites. This barrier can withstand the mechanical stress exerted by the dendrites during battery operation, preventing them from reaching the cathode and causing short circuits or other safety issues. Moreover, chemical stability of the separator is equally important as it ensures that the separator remains intact and does not react or degrade in the pres- ence of the electrolyte or other battery components. A chemically stable separator helps to prevent the formation of reactive species that can further promote dendrite growth. Researchers are actively exploring different materials and designs for separators to enhance their me- chanical strength and chemical stability. These efforts aim to create separators that can effectively block dendrite formation, thereby improving the safety and performance of lithium-ion batteries. While there are several research directions to address the issue of dendrite formation, using a separator with high mechanical strength and chem- ical stability is an important approach to prevent dendrites from infil- trating the cathode and ensure safe operation of lithium metal batteries. Several types of separators currently used in research include nanoporous polymer separators [16], ceramic composite separators [17], nanofiber separators [18-20], and metal-organic skeleton (MOF) separators [21-24]. While these separators have shown some ability to inhibit the growth of lithium dendrites, they still have some drawbacks,](https://i.kym-cdn.com/photos/images/masonry/002/774/796/ece.png)
![ELSEVIER Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Surfaces and Interfaces journal homepage: www.sciencedirect.com/journal/surfaces-and-interfaces The three-dimensional porous mesh structure of Cu-based metal-organic-framework - aramid cellulose separator enhances the electrochemical performance of lithium metal anode batteries Manshu Zhang, 1, Liming Wu, Tao Yang, Bing Zhu, Yangai Liu"." "Beijing Key Laboratory of Materials Utilization of Nonmetallic Minerals and Solid Wastes, National Laboratory of Mineral Materials, School of Materials Science and Technology, China University of Geosciences, Beijing 100083, China b College of Materials & Environmental Engineering, Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou 310036, China SURFACES INTERFACES ARTICLE INFO Keywords: Lithium metal battery Lithium dendrites CUMOF-ANFS separator ABSTRACT Lithium metal, due to its advantages of high theoretical capacity, low density and low electrochemical reaction potential, is used as a negative electrode material for batteries and brings great potential for the next generation of energy storage systems. However, the production of lithium metal dendrites makes the battery life low and poor safety, so lithium dendrites have been the biggest problem of lithium metal batteries. This study shows that the larger specific surface area and more pore structure of Cu-based metal-organic-framework - aramid cellulose (CUMOF-ANFS) composite separator can help to inhibit the formation of lithium dendrites. After 110 cycles at 1 mA/cm², the discharge capacity retention rate of the Li-Cu battery using the CuMOF-ANFS separator is about 96 %. Li-Li batteries can continue to maintain low hysteresis for 2000 h at the same current density. The results show that CUMOF-ANFS composite membrane can inhibit the generation of lithium dendrites and improve the cycle stability and cycle life of the battery. The three-dimensional (3D) porous mesh structure of CuMOF-ANFS separator provides a new perspective for the practical application of lithium metal battery. 1. Introduction Certainly, here is a possible introduction for your topic:Lithium- metal batteries are promising candidates for high-energy-density rechargeable batteries due to their low electrode potentials and high theoretical capacities [1,2]. However, during the cycle, dendrites forming on the lithium metal anode can cause a short circuit, which can affect the safety and life of the battery [3-9]. Therefore, researchers are indeed focusing on various aspects such as negative electrode structure [10], electrolyte additives [11,12], SEI film construction [13,14], and collector modification [15] to inhibit the formation of lithium dendrites. However, using a separator with high mechanical strength and chemical stability is another promising approach to prevent dendrites from infiltrating the cathode. By incorporating a separator with high me- chanical strength, it can act as a physical barrier to impede the growth of dendrites. This barrier can withstand the mechanical stress exerted by the dendrites during battery operation, preventing them from reaching the cathode and causing short circuits or other safety issues. Moreover, chemical stability of the separator is equally important as it ensures that the separator remains intact and does not react or degrade in the pres- ence of the electrolyte or other battery components. A chemically stable separator helps to prevent the formation of reactive species that can further promote dendrite growth. Researchers are actively exploring different materials and designs for separators to enhance their me- chanical strength and chemical stability. These efforts aim to create separators that can effectively block dendrite formation, thereby improving the safety and performance of lithium-ion batteries. While there are several research directions to address the issue of dendrite formation, using a separator with high mechanical strength and chem- ical stability is an important approach to prevent dendrites from infil- trating the cathode and ensure safe operation of lithium metal batteries. Several types of separators currently used in research include nanoporous polymer separators [16], ceramic composite separators [17], nanofiber separators [18-20], and metal-organic skeleton (MOF) separators [21-24]. While these separators have shown some ability to inhibit the growth of lithium dendrites, they still have some drawbacks,](https://i.kym-cdn.com/photos/images/original/002/774/796/ece.png)
FAIL / Epic Fail
These rose patterned bed sheets might not create the exact effect you were going for.


FAIL / Epic Fail
I think I see the problem.
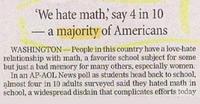

FAIL / Epic Fail
In numerical terms, this must be one of the biggest corrections ever made by a newspaper.


FAIL / Epic Fail
All 50 Ways


FAIL / Epic Fail
