| Navigation |
| About • History • Online Presence • Devices • Applications • Search Interest • External References • Recent Images • Recent Videos |
About
Augmented Reality (AR) is a live view of the real world as supplemented by computer-generated images, sound and other data that are geographically relevant. Beginning in the late 2000s, the commercial application of the technology has seen a substantial growth, particularly in the context of consumer electronics and gaming.
History
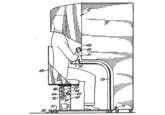
In computer science, the concept of augmented reality (AR), along with virtual reality (VR), has been a subject of discussion and experimentation since as early as the late 1950s with American cinematographer Morton Heilig's invention of a motorcycle simulator called Sensorama in 1962. The arcade-like machine was designed to provide an immersive cinematic experience of a cycle ride through the streets of Brooklyn, New York, complete with several sensory inputs that can simulate lifelike elements (shown below); the viewer could see the physical surroundings through a stereoscopic 3D environment, as well as feel the blowing wind and vibration of the seat in motion.

In 1966, Harvard University's electrical engineering professor Ivan Sutherland invented the first model of the head-mounted display (HMD), a hardware device that would later become a crucial component in both AR and VR technologies. In 1980, EyeTap, one of the first projects to utilize the HMD device in augmented reality software, was created by Steve Mann.[1]
Research & Development
The term itself was coined by American professor Tom Caudell in 1990 while working on a virtual reality software program for Boeing to assist in the aviation company's training, manufacturing and engineering processes. In 1992, two other milestone AR projects were unveiled; VIRTUAL FIXTURES, the first functioning AR guidance-assistance system developed by LB Rosenberg for the United States Air Force, and KARMA (Knowledge-based Augmented Reality for Maintenance Assistance), a prototype AR system based on a see-through head-mounted display (HMD) to assist in maintenance tasks for a laser printer.



Left to right: EyeTap, Sega VR and Virtual Boy
Commercialization
In 2011, Nintendo released its latest portable game console system Nintendo 3DS with pre-installed augmented reality abilities, which can be used in various Nintendo 3DS games as well. In 2013, Google announced the creation of Google Glass (similar to EyeTap), an augmented reality head-mounted display unit. In 2015, Microsoft announced "Windows Holographic" and "HoloLens", an augmented reality software and accompanying headset that use sensors and a processing unit to project "holograms" in the real world.
Online Presence
While the earliest use of the term predates the Internet, the augmented reality technology has generated a significant volume of discussions and public interest online since the beginning of its commercial application in the late 2000s. On October 27th, 2009, Urban Dictionary user darkfable defined augmented reality as "blurring the line between what's real and what's computer generated".[6] The augmented reality subreddit was created in 2010 and has collected over 2,000 subscribers as of May 2015.[8] Other virtual reality and augmented reality topics and devices also have their own devoted subreddits.
In addition, there have been numerous parodies about VR and AR devices. On April 19th, 2013, comedy duo Smosh uploaded a parody of Google Glass on YouTube that has received over 16 million views as of May 2015. On March 29, 2014, Marc Tschudi uploaded a parody of Oculus Rift after Oculus VR was bought by Facebook.
On April 5th, 2012, a post by Redditor BabyStevie reached the front page of the /r/AdviceAnimals subreddit titled "Why Google’s project “Glass” will be successful", featuring an early release photo for the project accompanied by the caption “No one has a clue / that I’m watching porn right now.”[9] On March 2015, a post by Redditor YaMB titled "The only practical use for virtual reality" had around 3,200 upvotes, featuring a picture of man who is about to have sexual intercourse with a woman while viewing "Cory in the House" with the Oculus Rift.[10]


Devices
Smart Glasses
Project Glass is a research and development program by the multinational Internet and software corporation Google, which aims to build an augmented reality head-mounted display unit. A promotional video released by Google in April of 2012 has inspired several parody videos and image macros.

Other Brands
- Sony SmartEyeglass
- Moverio BT-200 Epson
- Inforod
- Vuzix M100 Smart Glasses
- Mirama Prototype
- META Pro
- Zeal Optics Goggles
Smart Helmets
- Reevu Motorcycle Helmet
- Skully Smart Helmet
- DAQRI Smart Helmet
- Recon Jet
Smart Watches
- Apple Watch
- Samsung Galaxy Gear
- Sony Smartwatch
- Pebble Watch
Applications
EyeWriter
The EyeWriter is an augmented reality (AR) eye-tracking system comprised of low-cost cameras and open-source vision software that enables individuals with impairment in motor functions, such as ALS patients, to draw by processing the movement of their eyes. The wearable device was originally developed for Tony Quan (a.k.a Tempt), a Los Angeles-based graffiti artist who was diagnosed with Lou Gehrig's disease in 2003, by engineers and artists from the Free Art & Technology Lab, Graffiti Research Lab and OpenFrameworks, including Evan Roth.
Frenchising the Mona Lisa
In 2011, Iranian-born Canadian artist Amir Baradaran created Junaio, an augmented-reality mobile app that brings the subject of Leonardo Da Vinci's Mona Lisa to life on the screen with an animation of the iconic Italian lady placing a French flag scarf around her head like an Islamic hijab.
Far-Play
Far-Play (stylized fAR-Play, from augmented reality) is a software platform developed at the University of Alberta, for creating location-based, scavenger-hunt style games which use the GPS and web-connectivity features of a player's smartphone. According to the development team, “our long-term objective is to develop a general framework that supports the implementation of AARGs that are fun to play and also educational”
Alive
Alive is a mobile augmented reality software which was developed by Times Internet Ltd[1] and published in December 2012 as freeware. It has been developed for The Times of India and Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd. other publications and properties.[2][3][4] It uses the mobile device's video camera to recognise pre-trained images and overlay an image,video or 3D content on the recognition of image. Aliveapp is the only augmented reality application in the world to be available on the four major platforms(Android, iOS, Windows, Blackberry Symbian and Java) and is augmenting the complete newspaper.[5] It is the first publicly available application designed for a Newspaper Giant that used a location-based approach to Augmented Reality along with the image based Augmented Realit
XARMEX
XARMEX (short for: eXtended Augmented Reality for Military EXercise ) is an augmented reality-aided Close quarters combat simulation system, combining motion detection hardware with image overlay/stabilization software to create realistic military simulation environments and computer games.
Search Interest
External References
Wikipedia – Augmented reality
Urban Dictionary – Augmented reality
Reddit – Augmented Reality
Reddit – Why Google's project "Glass" will be successful /r/AdviceAnimals
Mashable – Augmented Reality
Wikipedia – List of Augmented Reality Software
Pocket Lint – The History of Augmented Reality
VRS.org – Virtual Reality Society
Microsoft – Hololens
WikiSpaces – Augmented Reality Education
Columbia University – KARMA
YouTube – Search Results for 'Augmented Reality'
iPhoneness – Augmented Relaity iPhone Applications


















Comments ( 63 )
Sorry, but you must activate your account to post a comment.
Please check your email for your activation code.