| Navigation |
| About • Origin • Spread • Search Interest • External References • Recent Images • Recent Videos |
About
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) is a method of cyberattack that usually involves temporarily blocking access to a website or server by flooding the bandwidth of a targeted network. The most common methods of DDoS include exploiting unprotected server networks, sending massive requests or opening multiple connections with the server.
Origin
The first publicly available DDoS tools Trinoo and Tribe Flood Network were released in 1997 and 1998 respectively.[8] The first well-documented DDoS attack took place in August 1999, which targeted a single University of Minnesota computer and knocked the system offline for more than two days. DDoS came grabbed public's attention months later in February 2000, after a number of high profile search portals and e-commerce sites were taken offline for hours, including Yahoo!, Amazon, Buy.com, CNN, eBay, E*Trade and ZDNet. In addition, several companies reported significant losses due to the downtime, with Yahoo! losing about $500,000 and costing Amazon nearly $600,000.[7]
Spread
According to The Next Web's timeline of DDoS attacks[6], most notable attempts in the first half of the 2000s were made by individuals using botnets and software programs. In 2001, Register.com came under a severe attack using tens of thousands of DNS records from around the world that lasted for an entire week.[9] In October 2002, all 13 Domain Name System root nameservers were targeted by a DDoS attack, which lasted for approximately one hour. In 2003, eBay was taken offline by a DDoS attack involving 20,000 computers, causing damage of at least $5,000.[10]


Beginning in the mid-2000s, DDoS tools became widely adopted by hackers, activists and even criminals for personal gains, leading to the creation of cyberattack task forces in law enforcement agences.
Cyberattacks on Estonia
In 2007, several government websites of Estonia were brought down by DDoS attacks originating from Russia, which further added to the diplomatic tension between the two countries building up at the time. The following year, Russian hackers and criminal were once again linked to similar attacks against websites of Georgian, Azerbaijani and Russian governments in the news.
Iranian Green Movement
In 2009, a crowdsourced, PHP-scripted DDoS attack took down several pro-Ahmadinejad websites during the protests of 2009 Iranian election, demonstrating its potential use in political activism.[6]
Operation Payback
Operation Payback is a series of DDoS attacks organized by members of Anonymous against a number of major entertainment websites including Recording Industry Association of America and the Motion Picture Association of America. The attacks began September 19th, 2010 and continued unabated for over a month.
Operation Avenge Assange
Operation Avenge Assange is a series of DDos assaults led by Anonymous against Paypal, Visa and MasterCard’s websites in denouncing their decision to suspend all transactions with WikiLeaks following the 2010 U.S. diplomatic cable leak. Some of the other targeted sites included Amazon, Swiss Postal Finance as well as a number of U.S. government websites and various cybersecurity contractor firms.
Lulzsec Campaign
Lulzsec (Lulz Security) is a hacking collective that carried out a series of DDoS and other hacking attacks against commercial and government websites between May and June 2011. Some of the most notable targets included Sony Pictures’ internal database, Central Intelligence Agency website and Federal Bureau of Investigation's contractor InfraGard.
Operation Antisec
Operation Antisec is an international hacktivist campaign launched by a coalition of Anonymous hackers including former members of Lulzsec. The operation officially began on June 20th, 2011 with DDoS attacks against UK’s Serious Organized Crime Agency (SOCA) and persisted for months targeting high-profile websites in private business, government and even military sectors.
Operation Israel
Operation Israel (also known as #OpIsrael) is an Anonymous hacktivist campaign launched in November 2012 to protest the Israeli Defense Forces’ Operation Pillar of Defense. On November 16th, 2012, as many as seven hundreds Israeli websites reportedly experienced temporary shutdowns and defacements on the homepage, including the Bank of Jerusalem, the Israeli Defense Ministry and the President’s official website.
Cyberbunker vs. SpamHaus
In March 2013, the Dutch web hosting company CyberBunker was added to the anti-spam blacklist maintained by The Spamhaus Project on the grounds that the company was hosting spammers. As early as on March 19th, the Domain Name System (DNS) servers of Spamhaus were targeted by a distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack at an unprecedented scale of 300 gigabits per second, which lasted for over a week. According to cyber-security expert Patrick Gilmore[13], its scale was reportedly sufficient to slow down the Internet around the world and temporarily interrupt streaming services like Netflix, making it the "largest publicly announced DDoS attack in the history of the Internet.”


In a BBC interview article[11] published on March 27th, Spamhaus' chief executive Steve Linford stated that its servers were able to withstand the DDoS attempts and that Cyberbunker, in collaboration with criminal gangs from Eastern Europe and Russia, was responsible for the attacks. The article also reported that the incident is being investigated by at least five different national cyber-police agencies around the world, though Cyberbunker has yet to make any official statements regarding the accusations. That same day, New York Times[12] also reported on the ongoing cyberwar, which included a quote from Sven Olaf Kamphuis, an Internet activist who claims to be a spokesman for the attackers, stating that Cyberbunker was retaliating against Spamhaus for "abusing their influence."
2016 Dyn Attack
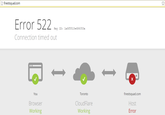
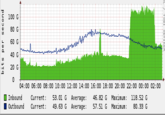
On the morning of October 21st, the Dyn DNS Company reported a global DDoS attack against their infrastructure.[22] As a result of the attack, several websites and services across the East Coast United States experienced outages, including Twitter, Spotify, Tumblr and Reddit. That day, Redditor hyperperforator submitted a post about the attack to /r/technology,[23] where Redditor raffraffraff replied with a series of graphs depicting the reported outages (shown below).

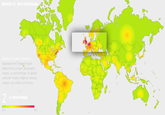
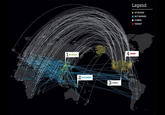
Meanwhile, the computer security blog KrebsonSecurity published an article noting that the size of these DDoS attacks had increased due to the widespread hijacking of poorly secured Internet of Things devices.[24] Meanwhile, the internet outage site DownDetector published a live-update map of the outages (shown below).

Tools
In 2008, the Low Orbit Ion Cannon (LOIC) DDoS software gained notoriety online when it was used by members of Anonymous to take down Scientology websites as part of Project Chanology.

On July 26th, 2010, the UDP flood attack tool UDP Unicorn was released on Sourceforge.[20] On October 29th, 2013, the information security website Infosec[21] published an article listing several different DDoS attack tools.
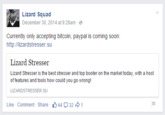
Lizard Stresser
On December 30th, 2014, the hacking group Lizard Squad announced[15] the released of their Lizard Stresser[14] tool, which allows users to pay a fee to have Lizard Squad DDoS an IP address. The website allows for the purchase of a range of services, including a 100-second attack for $5.99, an 8.5-hour-long attack for $129.99 and a 5-year package for $129.99.

On January 7th, the website 8chan was taken down in what was reported as a DDoS attack.[17] On January 8th, Lizard Squad took responsibility for the DDoS, claiming it was purchased using the Lizard Stresser tool.[18] On January 9th, the security news blog Krebs on Security[19] published an article about the attacks, speculating that the packets were being sent by a botnet made of home routers that had been infected with malware.
Search Interest
External References
[1] Wikipedia – Denial of Service Attack
[2] Gigenet Cloud – History of DDoS – Famous Attacks
[3] Armoraid – Understanding and surviving DDoS attacks
[4] CERT – Denial of Service Attacks
[5] ATLAS – Global Denial of Service Summary Report
[6] NextWeb – How DDoS attacks became the frontline tool of cyber-war
[7] Gary Kessler – Defenses Against Distributed Denial of Service Attacks
[8] UniForum Chicago – What's New in DDoS
[9] Secure64 – Register.com Suffers Week-Long DDoS Attack on DNS Servers
[10] The Register – Man admits to eBay DDoS attack
[11] BBC – Global internet slows after 'biggest attack in history'
[12] New York Times – Firm Is Accused of Sending Spam, and Fight Jams Internet&
[13] CloudFlare – The DDoS That Knocked Spamhaus Offline
[14] LizardStresser.su – Lizard Stresser
[15] Facebook – LizardSquadOnYaForehead
[16] Omnifeed – 4chan DDoSed by Lizard Squad
[18] Facebook – Lizard Squad
[19] Krebs On Security – Lizard Stresser Runs on Hacked Home Routers
[20] Sourceforge – UDP Unicorn
[21] Infosec Institute – DOS Attacks and Free DOS Attacking Tools
[22] Dyn – DDoS Attack Against Dyn Managed DNS
[23] Reddit – DDoS on DynDNS causing internet-wide outages
[24] KrebsonSecurity – DDoS on Dyn Impacts Twitter Spotify Reddit
Recent Videos 3 total
Recent Images 11 total
Share Pin








Comments ( 141 )
Sorry, but you must activate your account to post a comment.
Please check your email for your activation code.